Authentication methods
Pointsharp ID offers several types of authentication methods for user authentication, ranging from username/password to strong two-factor authentication.
All authentication methods will be stored under the Authentication tab. You can add new methods, edit, or remove existing.
| A default set of authentication methods are already configured. |
Add new methods if none of the pre-configured authentication methods suits the setup.
Pre-configured authentication methods
The combination of IP Address and Port must be unique for Pointsharp ID due to the nature of server software accepting requests on sockets.
Below are all pre-configured authentication methods:
- OATH
-
The OATH authentication performs authentication according to the OATH standard. The user enters an OTP received from the token, and the server validates the received OTP.
Pointsharp delivers software-based OATH tokens for all mobile platforms including Windows Phone, Android, iPhone and Java Mobile Edition. Additionally, Pointsharp also market hardware-based OATH tokens in various form factors.
- Password
-
The user enters username and password. Pointsharp ID will authenticate the user towards the configured User Storages.
This method can be used (in conjunction with Username Domain Removal function) when using Active Sync or to protect the Directory users from brute-force attacks.
- RADIUS
-
The user enters credentials for a legacy RADIUS-based authentication system, for example, RSA SecurID.
Pointsharp ID acts in this case as RADIUS proxy.
- SDK
-
Pointsharp SDK offers the ability to integrate and develop customer-defined authentication methods.
For further information on developing and deploying custom-built authentication methods consult the Pointsharp SDK documentation.
- SmartAuth
-
SmartAuth is a policy-driven authentication method, which decides what authentication method to authenticate the user with based on a policy framework.
- SMS
-
The user enters username and password, then a One-Time Password (OTP) is sent to the user. The user enters the OTP and is authenticated.
Add an authentication method
-
Start Pointsharp ID Admin GUI as an administrator.
-
Go to the Authentication tab.
-
Click Add and select the Authentication method in the menu.
-
Listener
-
Name: Set a name for the authentication method. This name is used in the Pointsharp ID audit log. The name is read only when the method is in use by a SmartAuth method.
-
IP Address: Set the IP address on which to accept the incoming authentication requests. (0.0.0.0 means all local addresses).
-
Port: Set the port for this authentication method to accept incoming authentication requests on. Ports are assigned from 18120 and up. An example of the port on the authentication method itself; this one is using "18134" but can be set to any port needed:
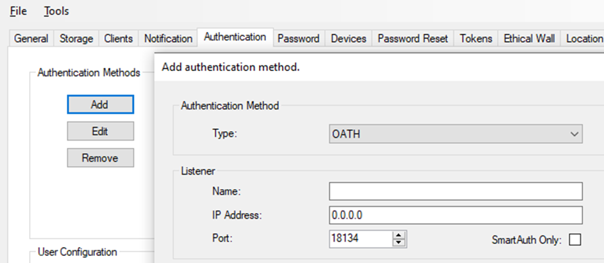
-
SmartAuth Only: Enable this to restrict the use of this method to only be from a SmartAuth-based authentication method. This will disable this method for RADIUS clients as well as all Pointsharp Web API clients. Default value is false, the SmartAuth Only function is disabled.
-
-
AD Account Check: Check this for enabling the Directory account status check. See AD account check.
-
Reply Message: Press this button to configure the reply messages that Pointsharp ID will communicate when challenging the user for further credentials. See Reply messages.
-
Under Additional settings, choose if Pointsharp password is to be used (if not, the Directory passwords will be used).
-
Enable User Domain Removal functionality if Pointsharp ID should remove any UPN suffix or
DOMAIN\prefixes in the incoming username. -
It is possible to delimit the allowed users for certain authentication methods in the Advanced Options. See Advanced options.
-
Use Cache Settings to configure Pointsharp ID to re-use past authentication decisions. This is useful if there is no need for the user to enter a new OTP in every authentication attempt. See Cache settings.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Apply.
-
Go to the General tab, click Restart. A Restart can be done from anywhere in the GUI by pressing CTRL-R.
| Press the Help button for detailed information on each field and function. |
AD account check
Check this for enabling the directory account status check.
| This feature requires that Pointsharp ID is configured against a Directory as User Storage, and that the communication is secured with SSL (LDAPS). |
When this is enabled and the Directory account is in the must change password state, the user will be challenged for the old password once again and challenged twice for a new password. The user will be authenticated and the password will be changed, if the old password was valid and the new password fulfill the password complexity policy.
Reply messages
Press this button to configure the textual reply messages that Pointsharp ID will communicate when challenging the user for further credentials, both in normal stateful authentication of a user’s identity, and in the password change challenge flow.
This message is set in the AuthenticationReply object received when calling the authentication service in Pointsharp ID Web services, as well as it is received in the RADIUS attribute Reply-Message when Pointsharp ID challenges the user for further credentials.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Challenge Message |
This is the reply message used when challenging the user for further credentials. For example the one-time password, either sent to the user in an SMS or obtained from the user’s OATH token. This value is used in the stateful SMS and OATH authentication. Default this is set to: |
Must Change Password |
This is the reply message used when the Directory account is in password change state. This message asks for the old password once more. Default this is set to: |
New Password |
This is the reply message used when the Directory account is in Default this is set to: |
New Password (again) |
This is the reply message used when the Directory account is in Default this is set to: |
Advanced options
It is possible to delimit the allowed users for certain authentication methods in Pointsharp ID, done in different ways depending on what User Storage a user resides in.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
User Storage List |
Manage the allowed User Storages by clicking Add and Remove. Use the Move Up and Move Down to re-order the policies. By default |
Alternate Username Attributes |
Enable this to make it possible to generate a list of attributes in order to alternate usernames for a user. If a user tries to authenticate with an alternate username, for example, an email address, then this list of attributes will be used to match the given username against all users' values for those attributes. If one match is found, then the matched user’s username will be used in the authentication procedure. Example 1. Alternate username
User |
User Attributes |
When enabled, the provided attributes are loaded for the authenticated user and sent back in the reply. This list is used to avoid too many calls to the user storage if the behaviour of the authentication procedure requires multiple values from the user. This is not applicable for SmartAuth based authentication methods. |
UPN Suffix |
When enabled, the UPN suffix will be used to create a UPN for the authenticated user and sent back in the reply. This is not applicable for SmartAuth based authentication methods. Example 2. UPN suffix usage
If UPN Suffix |
Cache settings
The Authentication Cache is optional and offers a mean to cache a successful authentication request for a user. That is, when the user re-uses the same password (or password combined with OTP) and found in the cache, the cached authentication decision is re-used.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Validity Interval (sec) |
Set this to the number of seconds that the Authentication Cache entry is valid before it is assumed to be expired. Default this is set to 86400 seconds (24 hours). Set this to 0 when the cache is to be valid forever. |
Usage Counter |
A cache entry is valid for a certain amount of authentications. Default set to 0, meaning that the cache can be used unlimited times. |
Re-authenticate when Expired |
Enable this to re-authenticate the credentials that are stored in the Authentication Cache entry when the entry is expired or usage limit is reached. Beware using this for authentication methods that may cause user account lockout, for example, the Directory authentication method. |
Legacy Cache |
Enable this to use the legacy cache included in pre-4.6 versions. In Pointsharp ID 4.7 and later, the legacy cache is replaced by a new cache implementation. |
Cache Length |
Enabled when the Legacy Cache is off. Enter number of cache entries that are allowed to serve as correct caches (default is 3). |
Cache Group |
Enabled when the Legacy Cache is off. Set the cache group to a name that will be the key for the cache. This value can be set for multiple authentication method cache settings to share the cache between multiple authentication methods. When this is enabled, the cache is always stored reversible (this can be overridden in the Reversible Cache setting). By default, this is left blank and not in use. |
Check Dropped Caches |
Enabled when the Legacy Cache is off. This is a helper function that is not changing the core functionality. The user authentication is rejected, but with this feature enabled it may for certain cases be possible to delimit the user locking function. Enable this flag to check among dropped cache values when the user is rejected. If a match is found the user will be rejected, but without increasing the user locking counters. The number of available dropped cache values are defined in the Cache Length setting. This feature can be useful if users have mobile devices that frequently retry with old (i.e. cache is dropped) credentials, which would normally result in the user account being locked. Enabled by default. |
Check Other Caches |
Enabled when the Legacy Cache is off. This is a helper function that is not changing the core functionality. The user authentication is rejected, but with this feature enabled it may for certain cases be possible to delimit the user locking function. Enable this flag to check cache values for all the other authentication methods when the user is rejected. If a match is found the user will be rejected, but without increasing the user locking counters. This feature can be useful if users accidentally use the wrong credentials for one method with credentials that have been used for another authentication method. Enabled by default. |
Cache OTP Only |
Enabled when the Legacy Cache is off. Applicable only for the OATH authentication method. Enable this flag to cache only the OTP, i.e. the password will be validated on all requests. |
Renew Caches |
Enable this to renew the timestamp on the valid cached credentials stored on the user. |
Renew Cache Group |
Set the name of the authentication method for which you want to enable the Renew Cache feature. This can also be set to the Cache Group name defined for other authentication methods. Empty by default. |
Email authentication
Similar configuration as for SMS can be also be done for email based authentication. See SMS authentication. The important part that differs from SMS is:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Type |
Select Email from the drop-down menu. |
Email Attribute |
Set this to mail. |
| The notification should be email based instead of SMS based notification. |
Enrollment
The Enrollment method can either perform authentication with configured authentication method for existing PSID user, or start a new user enrollment by setting a new Pointsharp password. After user setup, and login, a PointsharpLogin token and a default Time-based One-Time Password token will be created and sent to the Login Application.
See Simplified enrollment of the Login App for the enrollment method configurations.
FIDO authentication
The FIDO authentication method performs authentication with username and passwordless/password towards the defined User Storages for the client in question. If these are valid, then the user is challenged for a FIDO user verification. The user is authenticated if the user uses a valid FIDO security key.
| Ongoing user requests are stateful, i.e. the same browser window needs to be used. |
NTLM authentication
The NTLM authentication performs authentication with username and Pointsharp password towards the defined User Storages.
| NTLM follows the NTLM authentication protocol, and must only be used with Reversible Pointsharp Password or OTP. Enable Store Reversible Passwords under the Password tab. |
Password type
- Pointsharp password
-
The user must enter the Pointsharp password.
- Pointsharp password + OTP (appended)
-
The user must enter the Pointsharp password with a valid OATH OTP appended to it afterward.
- Pointsharp password + OTP (auto)
-
The user must enter a valid OATH OTP and the Pointsharp password. The server validates both ways automatically, that is PP+OTP and OTP+PP.
- OTP + Pointsharp password (prepended)
-
The user must enter a valid OATH OTP and the Pointsharp password appended to it afterward.
- Pointsharp password
-
The user must enter the Pointsharp password with a valid OATH OTP prepended to it in front of the password.
- OTP
-
The user must enter a valid OATH OTP.
| For this case the Pointsharp password is not used, i.e. the Pointsharp password setting Store Reversible Passwords is of no interest. |
- Windows password
-
The user must enter the Windows Password for authentication.
- Pointsharp password/Windows password
-
The user can enter the Pointsharp password or Windows password for authentication.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
OATH Window Size |
Set to the number of OATH OTPs that should be tested prior Pointsharp ID decides to reject the user. For example, by setting this to a value 100, Pointsharp ID calculates the next 100 OTPs and compares with the received OTP. If no match is found, the user is not authenticated. Default value is set to 25. |
Serial No Attribute |
Enable Live Provisioning by setting this attribute to a Directory attribute on the user object, containing serial numbers or OATH token types for all the OATH tokens to be deployed for the user.
This multivalued attribute value is separated with the character |
Windows Password URL |
Set the URL for Windows password authentication, the website can be an empty default site protected by Windows Authentication. |
Port (Windows Password URL) |
Set the port for Windows password URL to perform authentication on. |
Reject Windows Password |
Reject all positive Windows password and don’t lock user account. |
State Timeout (min) |
Timeout timer for NTLM handshake. Expire time for NTLM Type 2 challenge. |
OATH authentication
OATH is an open standard for strong authentication using one-time passwords. OATH authentications use a HMAC-based OTP algorithm. There are event based tokens which uses HOTP (RFC 4226), as well as time based tokens which uses TOTP (RFC 6238), to calculate the OTP. For more information about OATH, visit https://openauthentication.org.
- Token
-
OATH-based authentication requires a token to provide the OTP needed for a successful authentication. Each user needs to have a personalized token. For more information about tokens and the distribution of tokens to users, see separate section about Tokens.
| Press the Help button for detailed information on each field and function. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
OATH Window Size |
Set to the number of OATH OTPs that should be tested prior Pointsharp ID decides to reject the user. For example, by setting this to a value 100, Pointsharp ID calculates the next 100 OTPs and compares with the received OTP. If no match is found, the user is not authenticated. Default value is set to 25. |
Password Type |
Select the type of password mechanism to use, if any. Possible values are:
|
Auto Mode |
Enable this if appended password and OTP should be allowed both ways, i.e. password + OTP and OTP + password combined in the password field. This is only supported by:
|
Serial No. Attribute |
Enable Live Provisioning by setting this attribute to a Directory attribute on the user object, containing serial numbers and OATH Token types for all the OATH tokens to be deployed for the user.
This multivalued attribute value is separated with the character
This function can also be overridden by entering a hardcoded value which will be applied for all users.
For example setting the Serial No Attribute to |
Live provisioning
Live Provisioning is initiated whenever the user tries to authenticate for the first time with a specific authentication method. The serial number attribute value may contain any of the following values:
- MobileToken
-
An Android token is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending a OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- GoogleTOTP
-
A message of how to configure an Authenticator app is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending a OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
- GoogleHOTP
-
A message of how to configure an Authenticator app is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending a OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
- WindowsPhone
-
A Windows phone activation code is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending an OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- WindowsMobile
-
A Windows mobile token is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending an OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
- Java
-
A Java mobile token is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending an OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- JavaMobile
-
A Java mobile activation code is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending an OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- JavaStandard
-
A Java standard activation code is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending an OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- WindowsDesktop
-
A Windows desktop token is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending an OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- iPhone
-
An iPhone activation code is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending an OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- Android
-
An Android token is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending a OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- AndroidMarket
-
An Android market activation code is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending a OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
Prefix the value with pin: if the OATH token should be PIN-protected.
- MTP
-
A Multi-Time Password token is sent to the user by re-using the settings configured when sending a OATH token of this type to a user in Pointsharp ID Admin GUI.
- hardware:_serialnumber_
-
A Hardware token is retrieved from the OATH token retrieval framework (PSKC file, CSV file or from a plugin based on OATH retrieval API) based on the
_serialnumber_value. - mtp:_serialnumber_
-
A Multi-Time Password token is retrieved from the OATH token retrieval framework (PSKC file, CSV file or from a plugin based on OATH retrieval API) based on the
_serialnumber_value. - A serial number for a OATH token
-
When the Serial No Attribute contains a value that is not detected to be in line with the above matching rules, it is assumed to be a serial number for an OATH token. The token is retrieved from the OATH token retrieval framework (PSKC file, CSV file, or a plugin based on the OATH retrieval API) based on the serial number.
Use the attribute pager, which is not any of the matching rules listed above.
The attribute value windowsmobile|12345|pin:iPhone is thereby deployed, and sends an OATH token of type WindowsMobile to the user.
An OATH token with serial number 12345 is retrieved from the OATH token retrieval framework (PSKC file, CSV file, or a plugin based on the OATH retrieval API).
Finally, it sends a PIN-protected OATH token to the iPhone.
Password authentication
The password authentication performs authentication with username and password towards the defined user storages.
| Parameter | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Failed Password Cache |
Check this to enable the Last Failed Password cache on the user. This can be handy for example for ActiveSync devices that are incorrectly configured with an old password (or after a password change at the desktop PC). This user cache is persisted on the Pointsharp ID user and the cache is emptied by either authenticating with a new failed password, or by authenticating with the correct successful password.
|
||
Inject Pointsharp Password |
Only applicable when the option Pointsharp Password is enabled for the authentication method. If the user does not have a Pointsharp password stored, and the incoming credentials are correctly validated against the user storage, then that password will be injected as the user’s Pointsharp password. Default this feature is disabled and set to false. |
||
Device Check |
Only applicable for Pointsharp Access Gateway Device authentication methods. If the user has no Access Gateway Devices stored in Pointsharp storage, then the user is always rejected for this authentication method (with no failed login counter increase). By enabling this, the user will not be allowed to add any Access Gateway Devices automatically without forcing the use of the user portal or by permission by the administrator. Default this feature is disabled and set to false. |
PEAP (Wi-Fi) authentication
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) is a protocol for authentication in use in many environments such as Wi-Fi, LAN and so on.
The PEAP authentication method implements the so-called protocol PEAPv0-EAP-MSCHAPv2. In short, PEAP uses TLS to negotiate a secure channel from the authenticating peer, for example, the user’s PC, and Pointsharp ID. When the TLS tunnel is established, the peer and Pointsharp ID performs MSCHAPv2 authentication.
Note that for this authentication method to function, Pointsharp ID must be able to reversibly decrypt the user’s password in order to perform the MSCHAPv2 authentication step. In the Password tab, it is required that the Store Pointsharp Password Reversibly is enabled. Also beware that if the users already have deployed Pointsharp Password prior this configuration change, the checkbox Migrate Hashed Pointsharp Password may help whenever the user authenticates with the password, it is restored reversibly.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
PEAP MSCHAPv2 Server certificate (*.pfx) |
Pointsharp ID supports PEAP-MSCHAPv2 with an authentication method. PEAP uses certificates within the protocol; an SSL certificate with private key (and if needed the Certificate chain) must be configured. Click the Browse button to select the server certificate to use as the server certificate in the first PEAP phase. This requires to be a PFX file (PKCS12). When a file is selected, the file is copied to the <INSTALLATION>/bin/peap folder. Note that the issuer of the server certificate, that is the CA certificate, must be trusted at the authenticating peer. Either this CA must be installed by the user, or the user acknowledges it during authentication. The PFX file must contain a certificate with its private key. |
Password |
Enter the password to use, if any, when opening the PFX file. When a password is entered (or empty) press the Test button to verify that the configured password and PFX works and that the Pointsharp ID will be able to use the server certificate in the first PEAP phase. |
Password Type |
Wi-Fi connections do not support challenge response authentication so everything needed must be posted in one post. This limits the authentication methods to:
|
| Pointsharp Authentication cache can be used if the Wi-Fi network does a re-authentication often. The OTP will then be valid during the cache validity time and by that avoid forcing the user to re-authenticate. This problem does only occur when OTP is used. |
| The PEAP feature is an add-on to Pointsharp ID. |
RADIUS (proxy) authentication
| All RADIUS clients must be defined and configured under the Clients Tab, in order to use Pointsharp ID as an authentication server. The shared secret must be set on the client as well. |
RADIUS Mschap authentication
Use the specific Radius Mschap method if Mschap is a requirement.
This method offers the ability to add two-factor authentication in addition to the RADIUS MS-CHAPv2 authentication which is performed with a compliant RADIUS server.
The main difference between PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and Mschap configuration in the ID Server, is that the RADIUS client settings are needed in the authentication method itself.
SDK authentication
Pointsharp SDK leverages the possibility to integrate Pointsharp ID with any third-party application or other customer-specific system.
In order to deploy an authentication method, the plugin is developed with the SDK.
All plugin dll files are placed in the /plugins folder in the /bin folder.
-
Select the Plugin implementation to use for this authentication method.
SmartAuth authentication
SmartAuth is a policy-based authentication method. The SmartAuth policy-based framework is built on top of the existing authentication methods in Pointsharp ID, where the SmartAuth policies are evaluated and the user is dynamically re-directed to be authenticated based on the defined policy.
For example, users in a certain group are "allowed" authentication with a certain authentication method. All other users who do not meet this policy are authenticated using a different authentication method. Certain users may also be rejected due to too many authentication requests.
A few examples of what can be done:
-
Demand that users in a specific Organizational Unit must use OATH tokens, and users in another OU must use SMS (or other authentication options).
-
A specific user or users are only allowed a specific amount of devices.
-
A user’s specific device must use a certain authentication method.
-
Users that uses a specific country code are allowed or not allowed SMS, (+46 for example).
| Press the Help button for detailed information on each field and function. |
| Parameter | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Authentication Policy |
Manage the Authentication Policy. Press Add, Edit and Remove to manage, and use Move Up and Move Down to re-order the authentication policies. |
||||
SmartAuth Policy Settings |
This is the configuration for SmartAuth policy. SmartAuth offers a dynamic and versatile policy-based authentication framework which offers the possibility to authenticate users with different authentication methods based on user group memberships, user attributes, if the user has a Pointsharp password or if the user has a certain mobile phone with an installed OATH token. In the same policy list it is also possible to reject certain users or groups of users based on the same criteria. |
||||
Type |
Select the type for this SmartAuth policy. Select one of the following:
|
||||
Attribute Name |
Set the attribute name to use when evaluating this policy for the user in user storage. |
||||
Matching Pattern |
Enter the matching pattern to use when evaluating this policy for the user in user storage. The value can be combined with asterisks(\*) to configure Starts With, Ends With and Contains matches.
|
||||
Method |
Select the authentication method to use when this policy is successfully evaluated. These methods are defined in the Authentication tab in the Pointsharp ID Admin GUI. A SmartAuth authentication method can also be configured here, in order to perform another step of policy evaluation. |
CN=VPN-Users* will match if a memberOf attribute equals CN=VPN-Users,CN=Users,DC=acme,DC=com.
*@company.com will match if a mail attribute equals user@company.com.
*VPN-Users* will match if a memberOf attribute equals CN=VPN-Users,CN=Users,DC=acme,DC=com.
*-Users,CN=Users,DC=acme,DC=com will match if a memberOf attribute equals CN=VPN-Users,CN=Users,DC=acme,DC=com.
domain* will match all users authenticating with the DOMAIN\<username> syntax for policy type PsidUsername.
Note that the matching is not case-sensitive.
SMS authentication
Pointsharp ID has multiple authentication methods that send an OTP to the users; the OTP is required in the authentication of the users. Commonly these methods send the OTP as a mobile text message (SMS) to the user’s mobile device. The OTPs can be delivered by other notifications as well, such as email and custom notifications.
The SMS authentication method performs authentication with username and password towards the defined User Storages for the client in question. If these are valid, then the user is challenged for a one-time password (OTP). The OTP is sent to the user according to the defined notification method. The user is authenticated if the user enters correct OTP.
| Ongoing user requests are stateful, i.e. the same browser window must be used. This is done using the STATE attribute in RADIUS. |
| Press the Help button for detailed information on each field and function. |
| Parameter | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Mobile Number Attribute |
The user attribute to retrieve the mobile phone number (or email address) from. |
||
Alphabet |
The alphabet characters are used when random generating the OTP to the user. For example, if the OTPs should only contain random 1’s, 2’s, a’s and b’s, then set the alphabet to "12ab".
|
||
OTP Length |
The length of the OTP in number of characters. |
||
OTP Message |
The message used when distributing the OTP to the user. The {otp} is replaced with the OTP by Pointsharp ID. |
||
Primary Notification |
Notification used to send the OTP. |
||
Secondary Notification |
Notification used to send the OTP if the primary notification is unreachable. |
||
State Timeout |
The timeout in minutes for the state parameter. That is, the time interval until the user session is invalidated. |
||
OATH Failover |
If this value is set to something else than none, Pointsharp ID will allow an OATH OTP from the users token if the user did not receive the OTP via SMS. |